With healthcare costs on the rise, many organizations are exploring alternative insurance solutions to cover their employees. One of these options to potentially reduce and or control cost is a self funded insurance health plan. While this type of program is typically used by larger companies, many smaller-sized businesses have been opting to self-insure. Here are self funded health insurance pros and cons.
Let’s break it down:
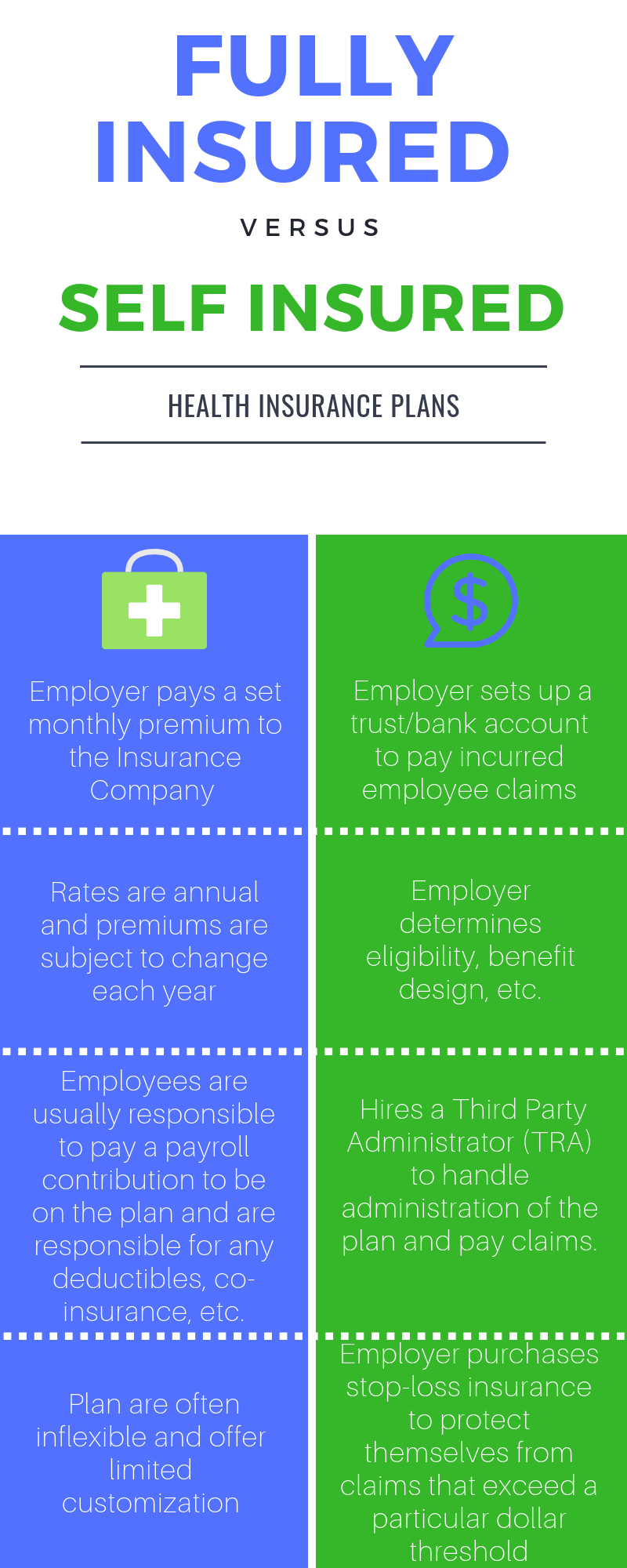
The Pros Self Funded Health Insurance:
1. Customized Plans
The most notable advantage of a self funded health insurance program is the ability to personalize your company’s plan. This means that you are able to determine and set forth eligibility, covered benefits, exclusions, policy limits and retiree benefits. These plans don’t have to comply with all of the state’s regulations that fully-insured plans do. These plans have to comply with federal mandates.
2. Retrieve and Analyze Data
By self-insuring, you claim all responsibility for your employee’s healthcare. Since you have access to claim information, your company can analyze this data in order to improve your insurance plans and even start a wellness program targeted to promote employee health. This can reduce the number of claims and cost.
3. Savings!
The most obvious! Self-funding has the potential to lower health insurance costs for you and your employees. Most sources state that it takes up to 5 years to see the cost benefits of these types of plans. With lower operation costs, and the ability to customize your plans, your business could see a savings between 4-20%. You also save money on the state taxes.
The Cons Self Funded Health Insurance:
1. Provision of Services and Administration
If you have a self-funded plan, you will have to hire a Third Party Administrator (TPA), often from an insurance carrier, who will handle servicing your employees’ health plan. While this can be more cost effective in the long run, you will have to monitor your TPA to ensure that services are being delivered properly.
2. Increased Risk
Although your company might save money, there are many risks associated with self-funded healthcare plans. Being that the Employer is responsible for the administration, servicing, and payout of employee claims, any failure to implement these services properly could result in breach of fiduciary duty. The Employer also must exercise thorough security measures to protect the privacy of data from claims and personal information.
3. Non-Renewal of Stop-Loss Coverage
One way to protect a self-funded plan from large claims is to insure the program by purchasing necessary stop-loss coverage. This type of insurance will kick in when an employee claim exceeds a specified dollar threshold. However, the policies are issued on an annual basis and renewal is not guaranteed. So if there are multiple employee claims, the carrier may issue a non-renewal, and it may be difficult to find coverage elsewhere. However, there are many more stop loss vendors than insurance carriers so the pool to purchase from is sizable.
4. Asset Exposure
Self-funded plans are only cost effective when there are minimal claims to pay out each year. That will not always be the case. There’s no way to predict employee claims, and you may find that your company is paying out more for insurance costs than it was with a fully funded plan. You can make sure you are protected by purchasing different layers of stop loss protection. When you run well, you retain the savings! If you’re fully insured, the insurance carrier holds reserves (extra premium) in case you decided to cancel your coverage.
So, is a self funded health insurance plan right for your business? If not, there maybe be other solutions to lower your employee benefits cost. Speak with your broker to find out more information. Any questions? Let’s talk!
Opinions expressed in this article are solely the author’s opinion, not intended to provide the reader with legal or any other professional advice. Should you need advice or opinion, consult with a qualified professional to address your specific needs.